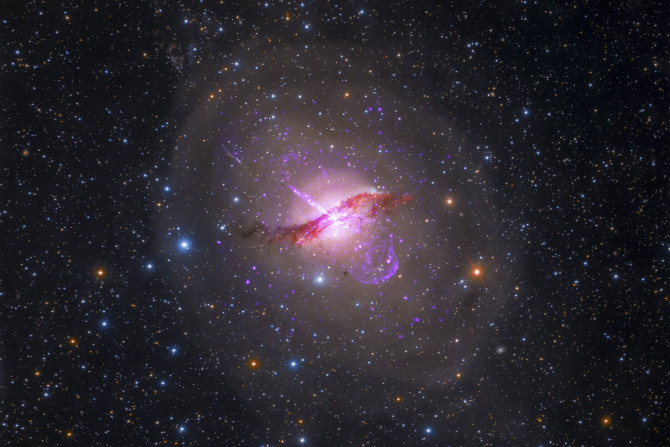
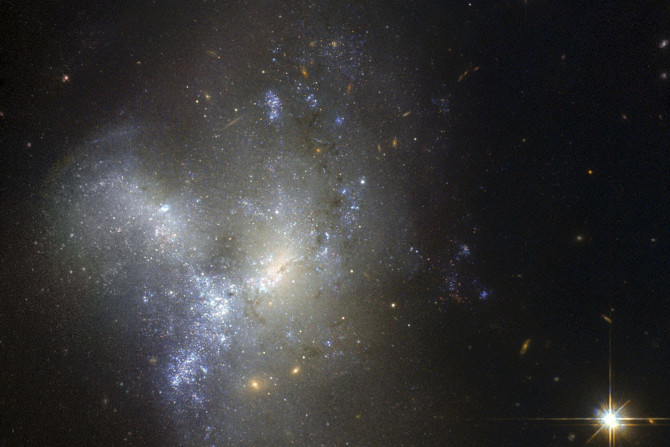
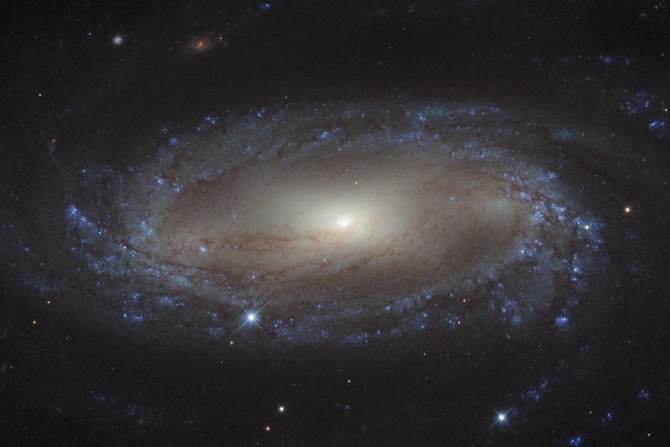
Astronomers have found out that a mysterious source of radio waves thought to be from a different galaxy is actually a binary star system containing a black hole and a low mass star. The discovery suggests that a huge number of black holes in our Galaxy Milky Way have gone unnoticed.
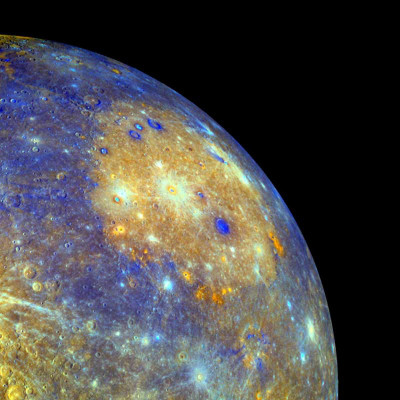
MIT geologists have studied part of planet Mercury’s cooling history right after it formed between 4.2-3.7 billion years ago and traced its origins to an enstatite chondrite, a rare meteorite. This kind of meteorite is extremely rare on Earth.
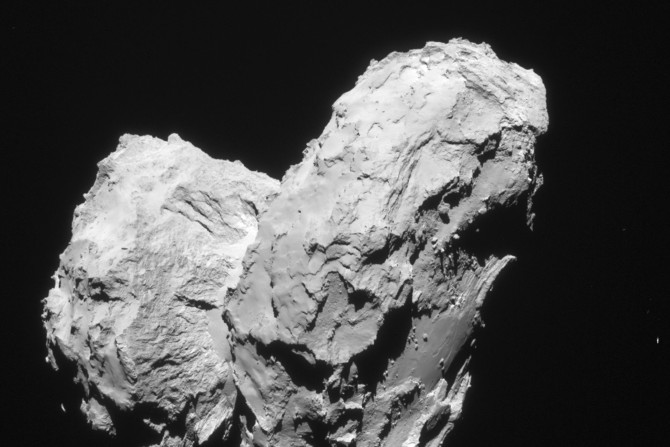
British researchers have developed a perfume that smells like a comet, particularly the 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, on which the European Space Agency (ESA) touched down in 2014.
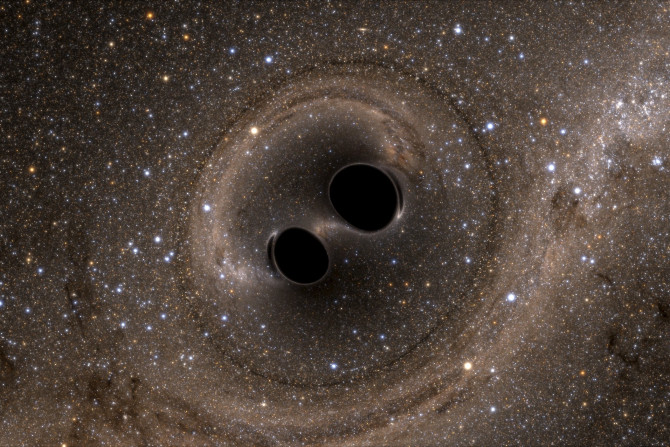
Scientists led by Durham University's Institute for Computational Cosmology captured gravitational waves via space-based detectors, and now they believe that these waves can help identify the origins of supermassive black holes. The scientist ran massive cosmological simulations that may be used to predict the rate at which gravitational waves caused by collisions between the monster black holes might be detected.
Scientists have discovered pieces of opal in a meteorite in Antarctica. The findings are extremely important for related studies on water and its life-forming abilities. According to a team of British researchers, the opal-studded meteorite is offering new clues as to the origins of life on Earth.
Researchers from Wageningen University in the Netherlands have revealed that cereals and vegetables they grew in “Martian” soil for two years are safe for human consumption. The Dutch researchers successfully raised peas, radishes, tomatoes and rye in soil that was made to match that of the red planet. This has provided researchers the hope of growing food on Mars. The food grown was found to contain “no dangerous levels” of heavy metals.
The Delta Aquarid meteor shower is coming, and Australians will be able to view the celestial event after its peak in late July. Like the recent Eta Aquarid meteor shower in May, the Delta Aquarid will be most visible in the Southern Hemisphere.
Astronomers from the University of Michigan and University of Maryland have for the first time mapped the flow of gas near a supermassive black hole, Swift J1644+57, that woke from its dormant state to destroy and devour a star that drifted close to it. The astronomers are the first to document X-rays bouncing from deep within the walls of the black hole’s newly-formed accretion disk after a tidal disruption event.
A Caribbean Sea study by ocean scientists from the University of Liverpool has revealed something very interesting. They discovered an area in the ocean that behaves like a whistle amidst all the noise of the ocean. The whistle is so loud that the noise can be heard from space in the form of oscillations of the Earth's gravity field.
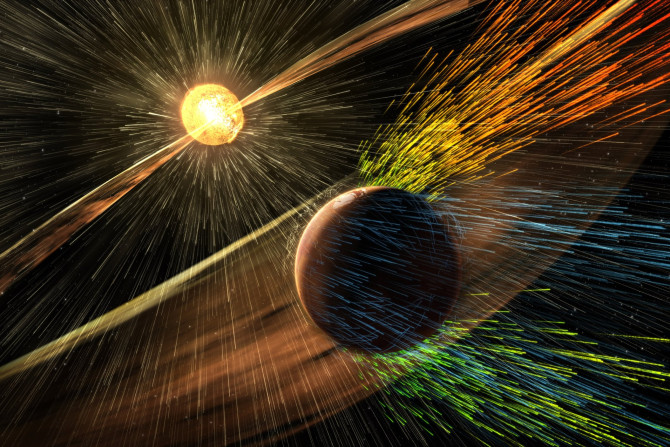
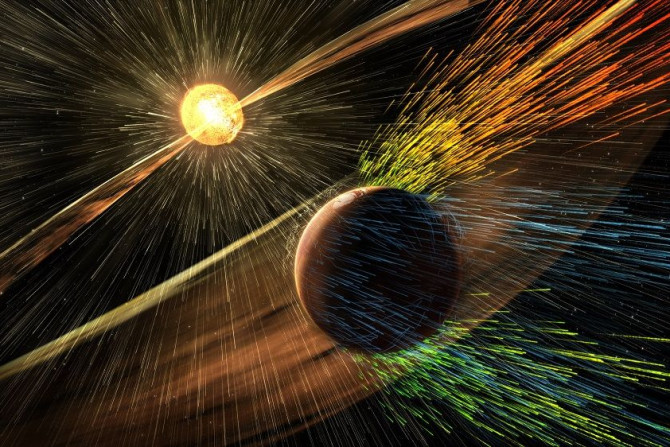
NASA has reported that an “electric wind” can strip Earth-like planets of oceans and atmosphere. The statement came after it was found out that planet Venus has an electric wind that is strong enough to remove components of water from its upper atmosphere.
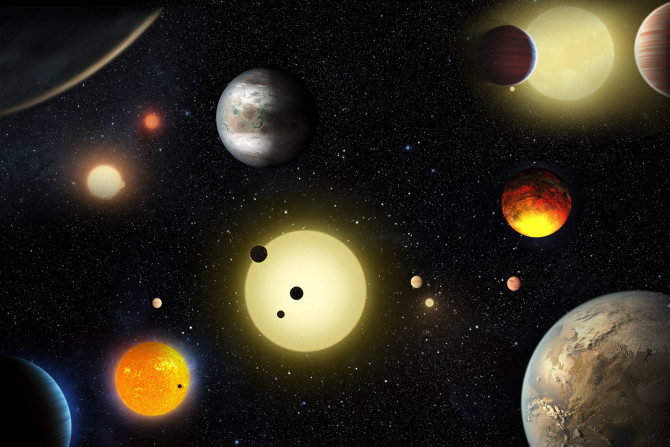
A team of international researchers have discovered the youngest fully-formed exoplanet ever known. The exoplanet orbits a young star 500 light years from Earth.
Scientists have detected life-giving gas oxygen in a faraway galaxy, 13.1 billion light years away. This could well be the oldest oxygen ever detected in the universe. The galaxy in question, SXDF-NB1006-2, is causing a storm in the scientific kingdom. Scientists are seeing the galaxy as it was 700 million years after birth of the universe. It shows the oldest signs of oxygen and this has baffled scientists.
A team of more than 1,000 scientists from more than 90 universities around the world has detected gravitational waves for the second time in history. The team also included Canberra scientists at the Australian National University (ANU).
Newly discovered baby planet PTFO8–8695 b in constellation Orion is slowly destroying itself and its close proximity to its sun is the cause, astronomers have pointed out. The likely new planet may be the galaxy’s youngest and is very unique as there is just 11 Earth hours in a year.
An international team of scientists used the Atacama Large Millimetre/submillimetre Array (ALMA) telescope in the Atacama Desert to get the first-ever glimpse of a supermassive black hole readying to gorge itself on gas clouds. The scientists spotted three clouds rushing towards the giant black hole at a tremendous speed of up to 1.3 million kilometres per hour.
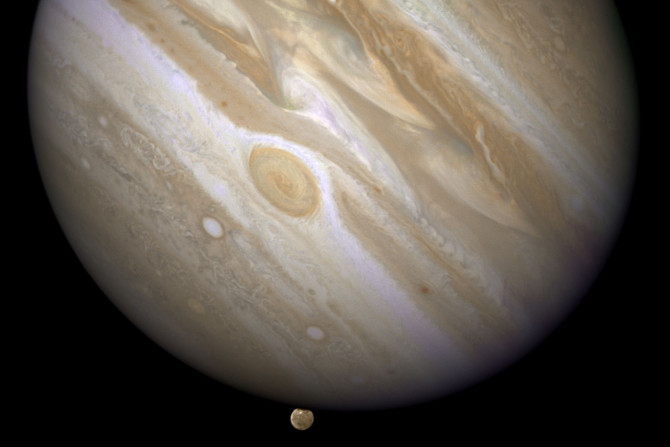
Using radio waves, scientists were able to get the clearest glimpse of what lies beneath Jupiter’s thick cloud tops. They found patterns of swirling ammonia mirroring those seen on the surface.
A mysterious force known as dark radiation may be making our universe expand way faster than previously anticipated. NASA made the discovery this week via its Hubble Space Telescope that revealed that the universe is expanding five to nine percent faster.
Scientists have detected a faint hydrogen signal emitted from a galaxy more than five billion light years away via Very Large Array (VLA) telescope in New Mexico, US. The international team of scientists that included an Australian radio astronomer from Perth believe that this find will push the boundaries of astronomy forward.
European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta spacecraft discovered ingredients glycine and phosphorous on a comet that are regarded crucial to the origins of life. Comets delivered chemical building blocks of life to Earth.
The new research suggests that Earth-like planet Kepler 62f would need a thick carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere to stop its water from freezing because of its distance from its star.
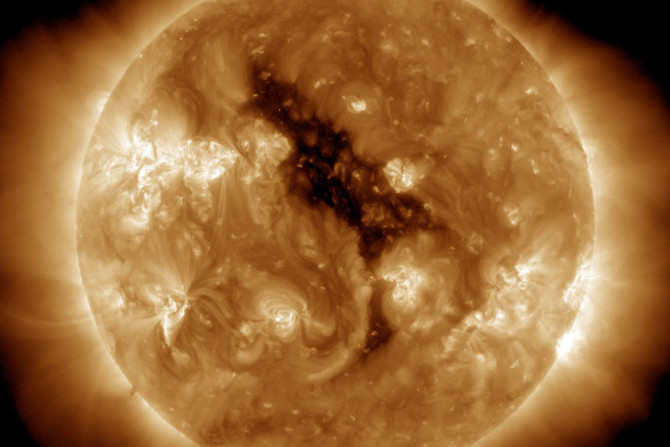
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) recently captured a massive hole on the sun’s surface. The gigantic coronal hole is blasting radioactive solar particles towards Earth.
Four billion years ago, Earth received only 70 percent of sun’s energy than what it receives today and should have been like an ice ball. Yet it was warm with liquid water.
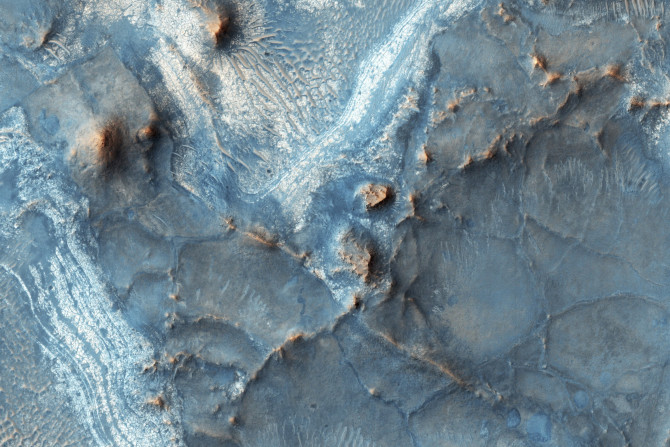
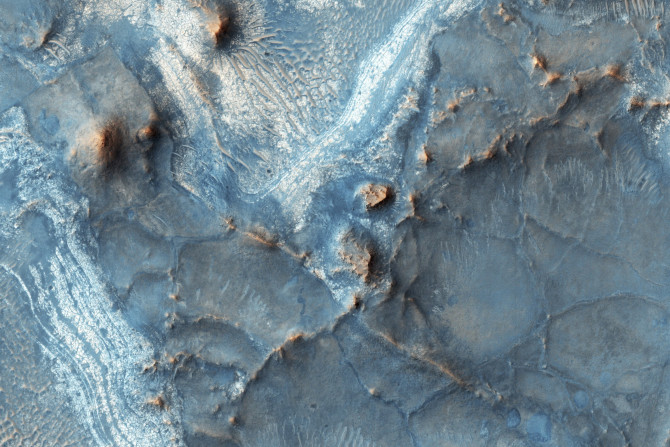
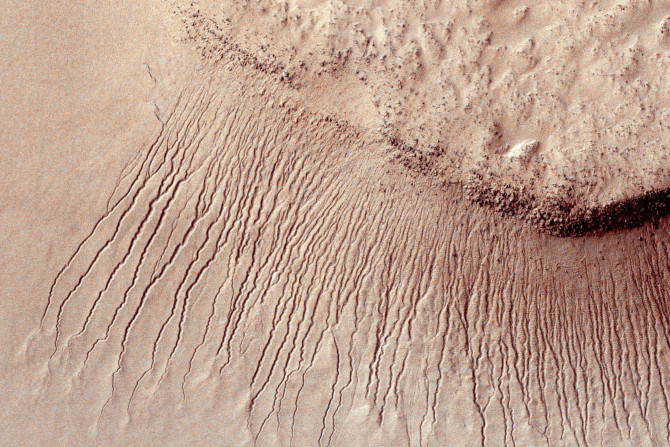
The three-billion-year-old mega-tsunamis in Mars caused waves that averaged 50 metres in height but rose up to the height of 30-storey buildings. They decimated shorelines and paced inwards.
Scientists may finally learn something about our Solar System’s origins after they discovered frozen comets orbiting a sun-like star (HD 181327). The researchers detected extremely low levels of carbon monoxide around the star.
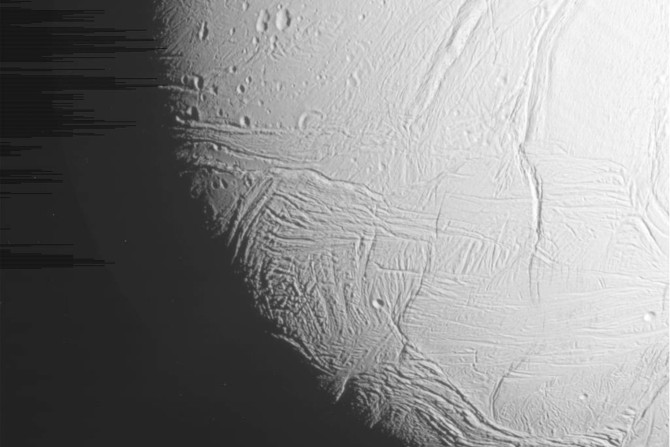
Europa and Enceladus may melt into ocean moons and any life-form, if at all they are hidden or trapped beneath the icy moons, may come to life in five billion years.
For the first time scientists found a way to sample the chemistry of ancient Earth's upper atmosphere. Surprisingly, the sampling indicated much higher concentrations of oxygen than expected.
New data from Swarm satellites suggest how changes in magnetic field of Earth may determine how space events such as solar storms will affect life in future.
SOFIA soars on a plane 45,000 feet above Earth. The discovery of atomic oxygen is immensely exciting as Mars is considered human’s potential new home.
Early earth’s oceans were bombarded by large meteors, comets and asteroids, which were responsible for planting the seeds of life that then took root after certain hydrothermal systems started operating.
Inside the Martian chamber, the melting ice produced liquid water that boiled energetically. It flowed down the slopes and then filtered into the sand.